Intrakavernous injection therapy is a well-established treatment for erectile dysfunction (ED). This method involves the direct injection of medication into the penis to enhance blood flow and facilitate an erection. In this section, we address common questions and concerns about this treatment option, including how it works, its effectiveness, potential side effects, and what to expect during the process.
Whether you’re considering this treatment or just seeking more information, these FAQs (frequently asked questions) provide essential insights to help you make informed decisions.
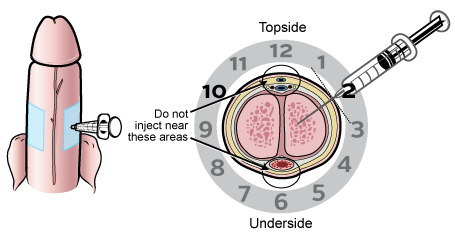
FAQs about intrakavernous injection for ED
ED patients sometimes need intracavernous penile injection. These patients are usually very worried about this issue. I tried to summarize the questions and answers frequently asked by our patients as follows:
What is an intrakavernous injection?
An intrakavernous injection involves administering medication directly into the cavernous bodies of the penis using a fine needle. This method is designed to increase blood flow, which helps achieve and maintain an erection.
How does intrakavernous injection work?
The injected medication, typically a vasodilator such as alprostadil, papaverine, or phentolamine, relaxes the smooth muscles and dilates blood vessels in the penis. This increased blood flow leads to an erection. The effect usually occurs within minutes after injection.
What medications are commonly used in intrakavernous injections?
Alprostadil: A prostaglandin E1 analog that dilates blood vessels and increases blood flow to the penis, commonly used alone or in combination with other agents.
Papaverine: A phosphodiesterase inhibitor that relaxes smooth muscle and enhances blood flow, often used in combination with other medications.
Phentolamine: An alpha-adrenergic blocker that dilates blood vessels and improves penile blood flow, typically used in combination with papaverine.
Trimix: A combination of alprostadil, papaverine, and phentolamine, designed to enhance efficacy and reduce side effects.
Bimix: A combination of papaverine and phentolamine, used when alprostadil is not suitable or as an alternative to Trimix.
What is the best agent for intrakavernous injection for ED and why?
The best agent for intracavernous injection for ED is alprostadil because it directly stimulates vasodilation and increases blood flow to the penis, leading to an erection. It has a high efficacy rate, quick onset, and fewer systemic side effects compared to other agents.
How effective is intrakavernous injection therapy?
Intrakavernous injections are highly effective for many men with erectile dysfunction. Success rates vary, but most patients experience satisfactory results, achieving an erection sufficient for intercourse in 70-80% of cases.
How is the injection administered?
The injection is typically self-administered using a prefilled syringe or vial. It is injected into the side of the penis, avoiding the urethra and the center of the shaft. Proper technique and hygiene are crucial for effectiveness and to minimize discomfort.
Are there any side effects or risks?
Common side effects include pain at the injection site, priapism (a prolonged erection), and slight bleeding or bruising. Rarely, systemic reactions such as dizziness or low blood pressure may occur. It’s important to follow instructions carefully to minimize risks.
How often can I use intrakavernous injections?
The frequency of use should be determined by a healthcare provider. Typically, injections should be spaced out to avoid complications such as priapism. Most guidelines suggest no more than 2-3 times per week.
What should I do if I experience priapism?
If you experience an erection lasting longer than 4 hours, seek medical attention immediately. Priapism can lead to serious complications if not treated promptly.
Can intrakavernous injections be used with other ED treatments?
Intrakavernous injections can sometimes be used in conjunction with other ED treatments, such as oral medications or vacuum pumps. However, combining treatments should be done under the guidance of a healthcare provider to avoid interactions and ensure safety.
How do I prepare for an intrakavernous injection?
Ensure you are familiar with the injection technique and have received proper training from your healthcare provider. Maintain good hygiene, use the correct dosage, and follow the recommended injection sites and schedule.
What are the indications for intrakavernous injection
Chronic ED: Effective for men with persistent ED who do not respond well to oral medications or other treatments.
Post-Prostatectomy: Useful for men who experience ED following prostate surgery, particularly when other treatments are ineffective.
Psychogenic ED: Beneficial for those with psychological causes of ED who do not achieve satisfactory results with psychological therapy alone.
Diabetic ED: Suitable for men with diabetes who have ED unresponsive to oral medications.
Vascular ED: Appropriate for individuals with ED due to vascular issues where other treatments have failed.
On-Demand Treatment: Provides a viable option for men seeking an effective, on-demand solution when other methods are not suitable.
Contraindications for intrakavernous injection
Hypersensitivity: Allergy or adverse reaction to the medication used in the injection.
Penile Conditions: Presence of penile deformities, such as Peyronie’s disease, or significant scarring that may affect injection efficacy or safety.
Severe Cardiovascular Conditions: Individuals with unstable angina, severe heart disease, or recent heart attack should avoid this treatment due to potential cardiovascular risks.
Sickle Cell Anemia: Risk of priapism and other complications in patients with sickle cell disease.
Priapism History: History of priapism (prolonged erections) that could be exacerbated by injections.
Use of Certain Medications: Concomitant use of medications that may interact adversely with injected drugs, such as certain anticoagulants or medications affecting blood pressure.
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Although generally not applicable to men, in contexts where the medication might affect a partner, such as in preconception or during breastfeeding, caution is advised..
Recommendations for best efficacy of intrakavernous injection
Proper Technique: Follow the correct injection technique and site as instructed by a healthcare provider to ensure effective medication delivery and minimize discomfort.
Pre-Injected Preparation: Ensure the medication is stored and prepared according to the manufacturer’s guidelines to maintain potency and safety.
Dosage Adjustment: Start with a lower dose and adjust based on response and tolerance to optimize efficacy and minimize side effects.
Injection Timing: Administer the injection approximately 5-20 minutes before sexual activity to allow adequate time for the medication to take effect.
Avoid Overuse: Limit the frequency of injections to avoid complications such as priapism and tissue damage; typically, no more than 2-3 times per week.
Monitor for Side Effects: Be vigilant for any side effects or unusual symptoms and report them to a healthcare provider promptly.
Combination Therapy: In some cases, combining injections with other ED treatments (under medical supervision) may enhance results.
Regular Follow-Up: Schedule regular check-ups with a healthcare provider to assess effectiveness, adjust dosages, and address any issues.
Lifestyle Factors: Maintain a healthy lifestyle, including managing underlying health conditions, to support overall efficacy of the treatment.
Side effects of intrakavernous injection
Pain at Injection Site: Discomfort or pain where the medication is injected.
Bruising: Minor bruising or bleeding at the injection site.
Priapism: Prolonged erection lasting more than 4 hours, which requires immediate medical attention to prevent complications.
Fibrosis: Formation of scar tissue in the penile tissue, potentially leading to changes in penile texture or curvature.
Edema: Swelling of the penis or surrounding tissues.
Dizziness: Lightheadedness or dizziness, particularly if the medication affects systemic blood pressure.
Penile Discoloration: Temporary changes in skin color or pigmentation of the penis.
Infection Risk: Potential for local infection if injection technique is not sterile.
Systemic Reactions: Rarely, reactions such as flushing, headaches, or hypotension may occur.
Summary
Intrakavernous injections are a direct and effective treatment for ED, involving the administration of medication into the penis to enhance blood flow and induce an erection. Commonly used medications include alprostadil, papaverine, and phentolamine. The process is typically straightforward and involves self-administration with proper technique. While effective for many, potential side effects include pain, bruising, and priapism. Frequency of use should be limited, and combining treatments should be done with medical guidance. For detailed guidance on how to administer injections and manage any side effects, consult with a urologist.
Prof. Dr. Emin ÖZBEK
Urologist
Istanbul- TURKIYE



Leave a Reply