Varicocele, a condition characterized by the enlargement of veins within the scrotum, can impact male fertility and cause discomfort. Various surgical interventions are available to address this issue, each with its own benefits and drawbacks. This comparison aims to evaluate the effectiveness, recovery times, and potential complications associated with different varicocele operations, including open surgery, laparoscopic surgery, and percutaneous embolization. By examining these methods, we seek to provide a comprehensive overview to guide patients and clinicians in selecting the most suitable approach for optimal outcomes.
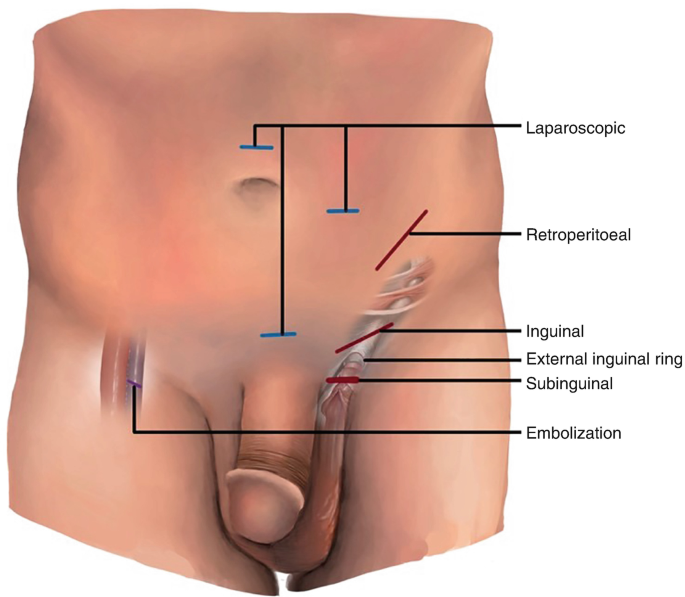
Types of varicocelectomy operations
For treating varicocele, several types of varicocelectomy operations are commonly used. Each has its own approach and specific indications. Here’s an overview of the main types:
- Open surgery: inguinal approach and retroperitoneal approach
- Microsurgery
- Laparoscopic surgery
- Percutaneous embolization
Comparison of varicocele surgeries
Each method has its own set of advantages and considerations, and the choice of procedure should be tailored to the individual patient’s needs and preferences. Here’s a detailed comparison of varicocele surgeries based on fertility outcomes, improvements in sperm parameters, recurrence rates, and complications:
Inguinal Approach:
- Fertility Outcomes: Generally effective in improving fertility, with significant improvement in sperm count and motility in a high percentage of patients.
- Sperm Parameters: Typically shows improvements in sperm count, motility, and morphology. Studies suggest a higher likelihood of positive outcomes compared to some other methods.
- Recurrence: Recurrence rates are relatively low but can occur, especially if not all affected veins are adequately addressed.
- Complications: Risks include infection, bleeding, testicular atrophy, and chronic pain. Postoperative pain and recovery time are generally longer than with minimally invasive methods.
Microsurgical varicocelectomy,
- Fertility Outcomes: Microsurgical varicocelectomy is highly effective in improving fertility outcomes. Many studies report substantial improvements in fertility rates post-surgery. The technique is known for its high success rate in achieving pregnancy, either spontaneously or through assisted reproductive technologies.
- Improvements in sperm parameters: Significant improvements in sperm count are frequently observed. Many patients experience a notable increase in the number of spermatozoa post-surgery. There is a marked enhancement in sperm motility. The improvement in motility is often reported to be better with microsurgical techniques compared to conventional open surgery. Improvements in sperm morphology are also commonly noted, contributing to overall enhanced sperm quality.
- Recurrence: Recurrence rates with microsurgical varicocelectomy are relatively low compared to other surgical techniques. The precise identification and ligation of affected veins reduce the likelihood of residual or recurrent varicoceles. The risk of recurrence is minimized by the meticulous approach and high resolution of the microscope, making it a reliable option for long-term success.
- Complications: Complications are relatively rare but may include infection, hematoma (blood collection), and chronic pain. The microsurgical approach typically results in fewer complications compared to traditional open surgery due to the enhanced precision. The risk of testicular atrophy (shrinkage) is lower with microsurgical techniques compared to more invasive methods. Other specific complications include injury to surrounding structures, but these are infrequent due to the high precision of the technique. Postoperative pain and recovery time are similar to open surgery.
Retroperitoneal Approach
- Fertility Outcomes: Similar to the inguinal approach, with improvements in fertility parameters reported.
- Sperm Parameters: Effective at improving sperm quality, often with lower recurrence rates compared to the inguinal approach.
- Recurrence: Lower recurrence rates due to better access to the veins.
- Complications: Risks are similar to the inguinal approach but may be less invasive with a lower risk of testicular atrophy.
Laparoscopic Surgery
- Fertility Outcomes: Effective in enhancing fertility outcomes, though some studies show slightly lower efficacy compared to open surgery.
- Sperm Parameters: Improvements in sperm count and motility are commonly observed. Results are generally favorable but may vary depending on the specific technique used.
- Recurrence: Recurrence rates are generally low, but slightly higher than with open retroperitoneal surgery.
- Complications: Risks include infection, bleeding, injury to surrounding structures, and less common issues like bowel obstruction. Recovery time is usually quicker compared to open surgery.
Percutaneous Embolization
- Fertility Outcomes: Effective in improving fertility, though some studies indicate slightly less dramatic improvements compared to surgical options.
- Sperm Parameters: Improvements in sperm count and motility are often reported, but results can be variable.
- Recurrence: Recurrence rates are low, but some patients may experience residual symptoms or require repeat procedures.
- Complications: Risks include allergic reactions to contrast material, infection, and, rarely, damage to surrounding tissues. Generally associated with fewer complications and shorter recovery time compared to surgical options.
Summary
Varicocele surgeries vary in approach and effectiveness. Microsurgical varicocelectomy stands out for its precision, offering excellent fertility outcomes, substantial improvements in sperm quality, low recurrence rates, and fewer complications, making it a highly effective and well-tolerated option.
Prof. Dr. Emin ÖZBEK
Urologist
Istanbul- TURKIYE



Leave a Reply