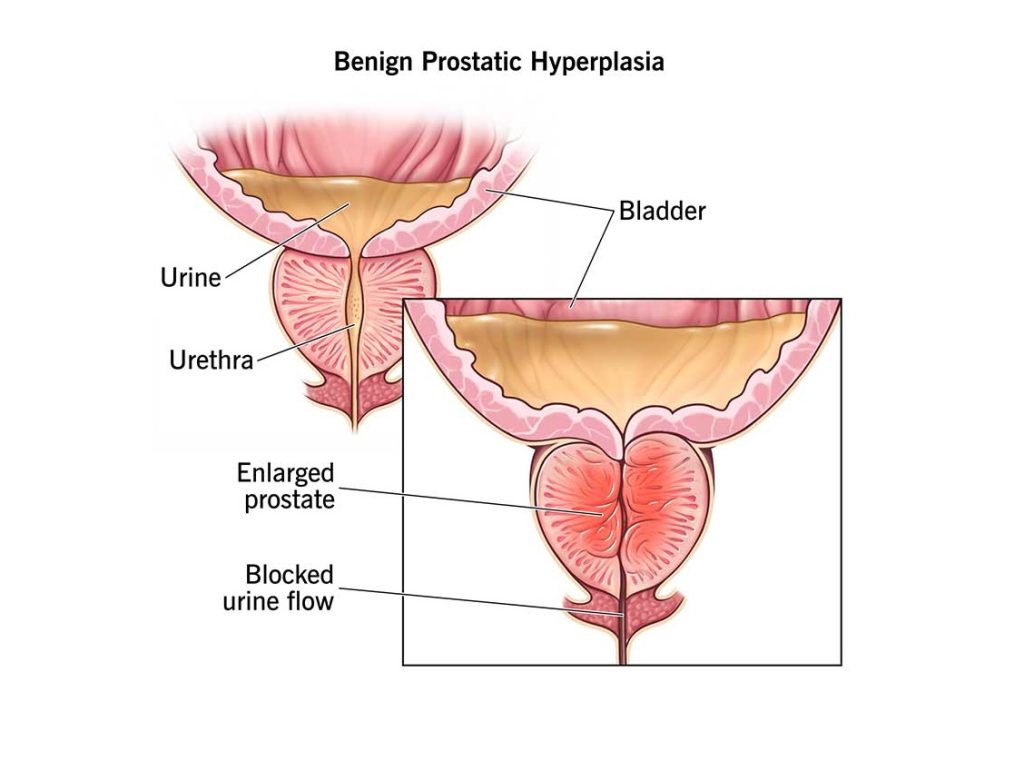
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) is a common condition in older men, characterized by an enlarged prostate gland that can lead to urinary difficulties. Several types of medications are used to treat BPH, aiming to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life.
These drugs include alpha-blockers, which relax the muscles in the prostate and bladder neck to ease urination; 5-alpha reductase inhibitors, which shrink the prostate by preventing hormonal changes; and combination therapies that utilize both classes for more comprehensive treatment. Additionally, newer medications and treatments continue to be developed, offering hope for more effective management of BPH.
Indications of medical therapy for BPH
Medical therapy for BPH is typically indicated based on the severity of symptoms, patient preferences, and the presence of complications or risk factors. The primary goal is to alleviate urinary symptoms, improve quality of life, and prevent complications associated with BPH. Here are the main indications for initiating medical therapy:
Moderate to Severe Symptoms:
- Patients with moderate to severe lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) that significantly impact their quality of life.
- Symptoms are often assessed using the International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS) or the American Urological Association Symptom Index (AUA-SI).
Patient Preference:
- Patients who prefer medical management over surgical options due to personal choice, fear of surgery, or when minimally invasive procedures are not an option.
Presence of Complications or Risk Factors:
- Recurrent urinary tract infections (UTIs)
- Bladder stones
- Renal insufficiency due to obstructive uropathy
- Recurrent hematuria (blood in the urine) due to BPH
- Acute urinary retention or high post-void residual urine volume.
Specific indications for different types of medical therapy
Here are the main spesific indications for medical therapy of BPH:
- Alpha-Blockers
- Patients with moderate to severe LUTS and relatively normal prostate size.
- Rapid symptom relief is desired.
- 5-Alpha Reductase Inhibitors
- Patients with moderate to severe LUTS and an enlarged prostate (usually >30-40 grams).
- Patients at risk of BPH progression or complications.
- Long-term therapy aimed at reducing prostate size and preventing disease progression.
- Alpha-blockers + 5-alpha reductase ınhibitors
- Patients with moderate to severe LUTS and a significantly enlarged prostate.
- Patients who do not respond adequately to monotherapy.
- High risk of disease progression and complications.
- PDE5 Inhibitors
- Patients with both BPH and erectile dysfunction (ED).
- Moderate to severe LUTS where combination with other medications (like alpha-blockers) is beneficial.
- Antimuscarinics
- Patients with predominant overactive bladder symptoms (urgency, frequency, nocturia) alongside BPH.
- Used cautiously in combination with other BPH medications due to the risk of acute urinary retention.
General information about drugs used to treat BPH
Several classes of medications are used to manage and treat BPH, each working through different mechanisms to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life.
- Alpha-Blockers
Examples: Tamsulosin, Alfuzosin, Doxazosin, Terazosin
Mechanism of Action: Alpha-blockers relax the smooth muscle in the prostate and bladder neck, making it easier to urinate.
Benefits: Rapid symptom relief, improvement in urine flow
Side Effects: Dizziness, fatigue, hypotension (low blood pressure), retrograde ejaculation
- 5-Alpha Reductase Inhibitors
Examples: Finasteride, Dutasteride
Mechanism of Action: These drugs inhibit the enzyme 5-alpha reductase, which converts testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone that promotes prostate growth. By reducing DHT levels
- Phythoterapy
Several herbal remedies have been studied and used traditionally to manage BPH. Here are some commonly used phytotherapeutic agents:
Saw Palmetto (Serenoa repens)
- Mechanism of Action: Inhibits 5-alpha reductase, reducing DHT levels, has anti-inflammatory properties and may reduce prostate swelling.
- Efficacy: Some studies suggest it can improve urinary symptoms and flow rates, but results are mixed.
- Side Effects: Generally well tolerated with mild gastrointestinal issues being the most common.
Beta-Sitosterol
- Mechanism of Action: A plant sterol that may improve urinary symptoms by reducing inflammation and enhancing urinary flow.
- Efficacy: Studies have shown improvement in urinary symptoms and flow measures.
- Side Effects: Rare and usually mild, such as gastrointestinal discomfort.
Pygeum (Prunus africana)
- Mechanism of Action: Extracts from the bark are believed to reduce inflammation and oxidative stress in the prostate.
- Efficacy: Some evidence suggests it can improve urinary symptoms and flow rates.
- Side Effects: Generally well tolerated with mild gastrointestinal issues reported.
Rye Grass Pollen Extract (Secale cereale)
- Mechanism of Action: Thought to reduce inflammation and improve muscle tone in the bladder and urethra.
- Efficacy: Some clinical trials indicate it may help reduce urinary symptoms and improve flow.
- Side Effects: Mild and infrequent, typically gastrointestinal issues.
Nettle Root (Urtica dioica)
- Mechanism of Action: Contains compounds that may inhibit the growth of prostate cells and reduce inflammation.
- Efficacy: Some studies suggest it can improve urinary symptoms, particularly when combined with other treatments.
- Side Effects: Generally well tolerated, with occasional reports of gastrointestinal discomfort.
- PDE5is
Phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors (PDE5 inhibitors) are a class of medications commonly used to treat erectile dysfunction. However, they have also shown efficacy in treating LUTS associated with BPH. Here’s an overview of PDE5 inhibitors used for BPH treatment:
Common PDE5 Inhibitors:
- Tadalafil (Cialis)
- Sildenafil (Viagra)
- Vardenafil (Levitra)
Mechanism of Action: PDE5 inhibitors work by blocking the enzyme phosphodiesterase type 5, which leads to increased levels of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP). This results in the relaxation of smooth muscle in the prostate, bladder, and associated blood vessels, improving blood flow and reducing urinary symptoms.
Benefits for BPH
- Symptom Relief: PDE5 inhibitors can reduce urinary symptoms such as frequency, urgency, and nocturia.
- Improved Urinary Flow: These medications can improve urinary flow and reduce the feeling of incomplete bladder emptying.
- Dual Benefit: Men with both BPH and erectile dysfunction may benefit from the dual action of PDE5 inhibitors, improving both urinary and sexual function.
Efficacy
- Tadalafil: Tadalafil is the most commonly studied PDE5 inhibitor for BPH. Clinical trials have shown that daily use of tadalafil can significantly improve BPH symptoms and urinary flow rates.
- Sildenafil and Vardenafil: While primarily used for erectile dysfunction, some studies suggest these drugs may also help with BPH symptoms, though they are not as well-studied as tadalafil in this context.
Side Effects
- Headache
- Flushing
- Indigestion
- Nasal congestion
- Back pain (specific to tadalafil)
Considerations
- Drug Interactions: PDE5 inhibitors can interact with nitrates and certain blood pressure medications, leading to dangerous drops in blood pressure.
- Not for All Patients: Patients with certain cardiovascular conditions should use PDE5 inhibitors with caution and under medical supervision.
- Combination Therapy: PDE5 inhibitors can be used in combination with other BPH medications, tuch as alpha-blockers, for enhanced symptom relief.
- Antimuscarinic agents
Antimuscarinic agents are a class of medications primarily used to treat OAB symptoms, which can co-occur with BPH. These symptoms include urgency, frequency, and nocturia. When used in the context of BPH, antimuscarinics can help manage irritative urinary symptoms, providing relief for patients who do not respond adequately to other BPH treatments alone.
Common Antimuscarinic Agents
- Oxybutynin
- Tolterodine
- Solifenacin
- Darifenacin
- Fesoterodine
- Trospium
Mechanism of Action: Antimuscarinic drugs work by blocking muscarinic receptors in the bladder, which reduces bladder muscle contractions. This helps to:
- Decrease the urgency and frequency of urination.
- Reduce nocturia (frequent urination at night).
- Improve overall bladder storage capacity.
Indications
Antimuscarinic therapy is indicated for:
- Patients with BPH who experience significant overactive bladder symptoms.
- Patients who have not achieved sufficient symptom control with standard BPH treatments such as alpha-blockers or 5-alpha reductase inhibitors.
Benefits
- Symptom Relief: Effective in reducing urgency, frequency, and nocturia.
- Quality of Life: Improved due to decreased irritative urinary symptoms.
Side Effects
Common side effects of antimuscarinics include:
- Dry mouth
- Constipation
- Blurred vision
- Dizziness
- Urinary retention (especially a concern in patients with significant bladder outlet obstruction)
Considerations and Cautions
- Risk of Urinary Retention: Antimuscarinics can exacerbate urinary retention in patients with significant bladder outlet obstruction. Therefore, they should be used cautiously and under medical supervision.
- Combination Therapy: Often used in combination with other BPH medications, such as alpha-blockers, to balance the reduction in irritative symptoms without significantly worsening obstructive symptoms.
Combination therapy of BPH
Combination medical therapy for BPH involves using more than one type of medication to manage symptoms more effectively than with monotherapy. This approach is often considered for patients with moderate to severe symptoms or those who do not respond adequately to a single medication. The most common combinations include alpha-blockers, 5-alpha reductase inhibitors, and sometimes PDE5 inhibitors. These are:
- Alpha-Blockers and 5-Alpha Reductase Inhibitors
Mechanism of Action:
- Alpha-Blockers: Relax the muscles in the prostate and bladder neck, providing rapid relief from urinary symptoms.
- 5-Alpha Reductase Inhibitors: Reduce the size of the prostate over time by inhibiting the conversion of testosterone to DHT.
Benefits:
- Alpha-blockers provide quick symptom relief, while 5-alpha reductase inhibitors offer long-term reduction in prostate size and symptom improvement.
- The combination can be more effective in reducing symptoms and preventing disease progression than either drug alone.
- Alpha-Blockers and PDE5 Inhibitors
Mechanism of Action:
- Alpha-Blockers: Relax smooth muscle in the prostate and bladder neck to improve urine flow.
- PDE5 Inhibitors: Enhance smooth muscle relaxation and blood flow in the lower urinary tract and prostate.
Benefits:
- Improved urinary symptoms and quality of life, especially in patients who also suffer from erectile dysfunction.
- PDE5 inhibitors can enhance the overall effectiveness of alpha-blockers.
- 5-Alpha Reductase Inhibitors and PDE5 Inhibitors
Mechanism of Action:
- 5-Alpha Reductase Inhibitors: Reduce prostate size by inhibiting DHT.
- PDE5 Inhibitors: Improve smooth muscle relaxation and blood flow, aiding in urinary symptom relief.
Benefits:
- Long-term reduction in prostate size with concurrent improvement in urinary symptoms.
- May benefit patients with both BPH and erectile dysfunction.
- Other combinations: Combination of antimuscarinic with alpha reductase ınhibitors, pde5 ınhibitors and alpha-blockers.
Summary
BPH is a common condition in older men characterized by an enlarged prostate gland, which can cause urinary symptoms such as difficulty in starting urination, weak stream, and frequent urination. Medical therapy for BPH aims to alleviate these symptoms and improve the quality of life. Drugs used to treat BPH include: Alpha-blockers, 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors and combination therapy.
Prof. Dr. Emin ÖZBEK
Urologist
Istanbul-TURKIYE



Leave a Reply