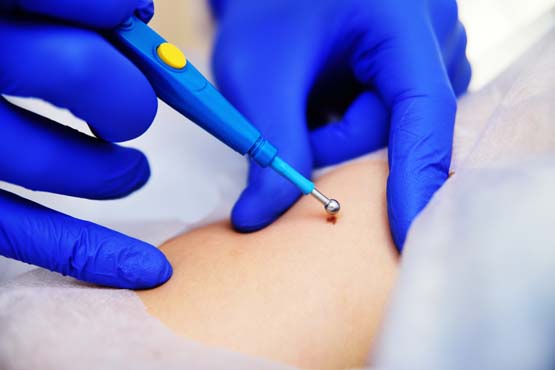
Electrocauterization is a common medical procedure used to treat genital HPV (Human Papillomavirus) warts. This treatment involves using heat from an electrical current to remove or destroy the warts. In this FAQs (frequently asked questions) section, we address common questions related to the electrocauterization process, its effectiveness, potential side effects, and what patients can expect during and after the procedure.
Whether you’re considering this treatment or want to know more about it, these FAQs provide helpful insights and guidance.
FAQs and answers about electrocauterization of HPV
Here are some frequently asked questions (FAQs) about the electrocauterization of genital HPV (warts):
1. What is electrocauterization?
Electrocauterization is a medical procedure that uses a heated electrical current to remove or destroy abnormal tissue, such as genital warts caused by HPV (Human Papillomavirus). The heat effectively cauterizes the wart, leading to its removal or shrinkage.
2. Is electrocauterization effective for treating genital warts?
Yes, electrocauterization is a highly effective treatment for genital warts. It is commonly used to remove visible warts and can be particularly helpful for larger or more difficult-to-treat warts.
3. Is the procedure painful?
The procedure is generally well-tolerated, but it may cause some discomfort or pain. Local anesthesia is typically applied to numb the area, which helps minimize pain during the procedure. Afterward, patients may experience mild to moderate pain or soreness that can usually be managed with over-the-counter pain relievers.
4. How long does the cauterization procedure take?
The procedure typically takes between 15 to 30 minutes, depending on the size and number of warts being treated. It is usually performed on an outpatient basis, meaning you can go home the same day.
5. What should I expect after the procedure?
After electrocauterization, you may experience swelling, redness, or discomfort in the treated area. This is normal and typically resolves within a few days. It’s essential to avoid touching, scratching, or picking at the area to prevent infection or scarring.
6. Are there any risks or side effects?
Like any medical procedure, electrocauterization has some risks, including infection, scarring, or changes in skin pigmentation. However, these complications are rare when the procedure is performed by a skilled healthcare provider.
7. How long does it take to heal?
Healing times can vary depending on the individual and the extent of the treatment. Most patients will experience complete healing within 2 to 4 weeks, but it may take longer for larger or multiple warts.
8. Can the warts come back after electrocauterization?
While electrocauterization is effective at removing warts, it does not cure the underlying HPV infection. There is a chance that new warts may develop in the future. It’s essential to follow your doctor’s advice for follow-up care and monitoring.
9. Are there any alternatives to electrocauterization for treating genital warts?
Yes, there are several alternative treatments for genital warts, including topical medications, cryotherapy (freezing), laser therapy, and surgical removal. Your healthcare provider will recommend the most appropriate treatment based on the number, size, and location of the warts.
10. Will I be contagious after the procedure?
Yes, you can still be contagious after the procedure since the HPV infection may remain in your body. It is essential to avoid sexual contact or use protection (such as condoms) to reduce the risk of transmitting the virus to others while healing.
11. How can I prevent genital warts in the future?
The best way to prevent genital warts is by getting the HPV vaccine, which protects against the strains of HPV that most commonly cause genital warts. Additionally, practicing safe sex by using condoms can reduce the risk of HPV transmission.
12. Is electrocauterization covered by insurance?
Coverage for electrocauterization may vary depending on your insurance provider and policy. It’s advisable to check with your insurance company beforehand to determine if the procedure is covered under your plan.
13. How electrocautery can help treat HPV?
Electrocautery can help treat HPV by using a heated electrical current to remove or destroy genital warts caused by the virus. This procedure effectively eliminates visible warts, reducing symptoms and preventing the spread of the infection in the treated area. However, it doesn’t cure the underlying HPV infection, so new warts may develop over time.
14. What’s the long-term outlook after electrocauterization?
The long-term outlook for those who receive electrocauterization for genital warts is generally positive, with most patients experiencing successful removal of warts. However, since the underlying HPV infection remains, new warts may develop in the future. Regular follow-up care and safe sex practices are important to manage the condition and reduce the risk of recurrence.
15. Is electrocauterization safe?
Yes, electrocauterization is generally safe when performed by a trained healthcare professional. While it carries some risks, such as infection or scarring, these are rare and can be minimized with proper care and aftercare instructions.
16. Is HPV vaccination possible after electrocauterization?
Yes, HPV vaccination is possible after electrocauterization. In fact, getting vaccinated can help protect against other strains of HPV and reduce the risk of future warts or HPV-related cancers, even after the procedure. It’s best to discuss the timing with your healthcare provider.
17. Are materials after electrocauterization need to be examined pathologically?
In most cases, materials removed during electrocauterization, such as genital warts, are not routinely sent for pathological examination unless there is a concern about unusual growth or potential cancerous changes. Your healthcare provider will determine if pathology testing is necessary based on the specific case.
18. If there are many warts one session or different sessions are needed?
If there are many warts, multiple sessions of electrocauterization may be needed to effectively treat them. The number of sessions depends on the size, number, and location of the warts, as well as how well the area heals after each treatment. Your healthcare provider will determine the best approach.
19. After Electrocauterization of Genital HPV (Warts) how many days sex is possible?
It is generally recommended to avoid sexual activity for at least 2 to 4 weeks after electrocauterization of genital HPV warts to allow the area to heal properly and reduce the risk of irritation or infection. Always follow your healthcare provider’s specific advice regarding when it’s safe to resume sexual activity.
Summary
Electrocauterization is a safe and effective procedure for treating genital warts caused by HPV. It uses heat from an electrical current to remove or destroy the warts. The procedure is generally well-tolerated, though mild pain or discomfort may occur. Local anesthesia is usually applied to minimize discomfort. While electrocauterization effectively removes warts, it does not cure the underlying HPV infection, so new warts may develop in the future.
Prof. Dr. Emin ÖZBEK
Urologist
Istanbul- TURKIYE



Leave a Reply