A testicular prosthesis is an artificial implant designed to replace a missing or removed testicle. These prostheses are often used for men who have lost a testicle due to injury, disease, or surgery. Here are some frequently asked questions (FAQs) about testicular prostheses to help you understand this medical device better. Understanding these key points can help you make an informed decision if you or someone you know is considering a testicular prosthesis. For more detailed information, it’s best to consult with a urologist.
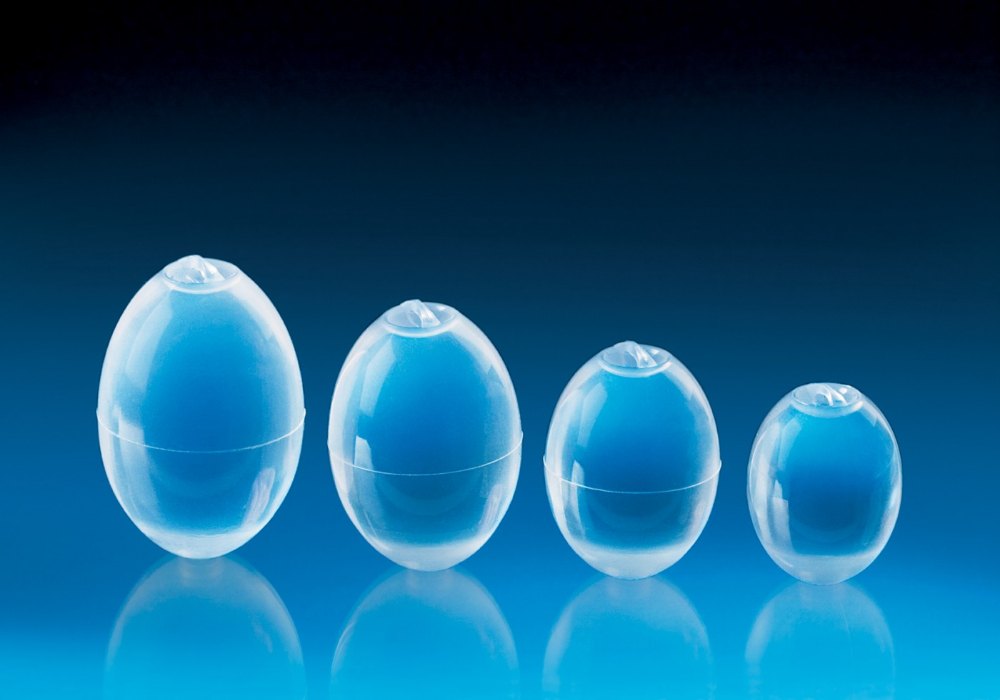
We generally place testicular prostheses on patients whose testicles have been removed due to testicular cancer. In this way, the patient does not need to receive anesthesia a second time.
FAQs about testicular prosthesis
A testicular prosthesis is an artificial implant designed to mimic the appearance and feel of a natural testicle, primarily used for cosmetic and psychological reasons. Below are detailed answers to some frequently asked questions (FAQs) about testicular prostheses.
1. What is a testicular prosthesis?
A testicular prosthesis is a medical device made of silicone, either solid or gel-filled, designed to replicate the size, shape, and consistency of a natural testicle. The primary purpose of a testicular prosthesis is to restore the appearance of the scrotum after a testicle has been removed.
2. Who might need a testicular prosthesis?
Men who have had a testicle removed due to various reasons might opt for a prosthesis. Common scenarios include:
- Testicular cancer: After orchiectomy (surgical removal of a testicle) due to cancer.
- Injury or trauma: Severe damage to the testicle that necessitates removal.
- Undescended testicle: In cases where an undescended testicle is removed surgically.
- Infection or disease: Other medical conditions that lead to testicular loss.
3. How is the prosthesis implanted?
The procedure for implanting a testicular prosthesis involves several steps:
- Pre-surgery: A consultation with a urologist to discuss the type and size of the prosthesis and assess overall health.
- Surgery: Conducted under general or local anesthesia, a small incision is made in the scrotum. The prosthesis is then inserted into the scrotal sac and positioned appropriately.
- Post-surgery: The incision is closed with sutures. The patient may need to rest and avoid strenuous activities for a few weeks to ensure proper healing.
4. Are there different types of testicular prostheses?
Yes, there are several types and sizes available:
- Silicone gel-filled prostheses: These provide a more natural feel and are the most commonly used.
- Solid silicone prostheses: These are firmer and less likely to rupture.
- Customized prostheses: Can be made to match the size and shape of the remaining testicle for a more natural appearance.
5. What are the benefits of getting a testicular prosthesis?
The benefits include:
- Cosmetic appearance: Restores the natural look of the scrotum, which can be important for personal confidence.
- Psychological benefits: Improved self-esteem and body image.
- Symmetry: Provides balance to the scrotal sac, which can be aesthetically pleasing.
6. Are there any risks or complications?
While generally safe, there are some risks associated with testicular prosthesis implantation:
- Infection: As with any surgery, there is a risk of infection at the incision site.
- Rejection or extrusion: The body may reject the implant, or it may shift out of place.
- Pain or discomfort: Some men may experience pain or discomfort after the surgery, though this typically subsides.
- Capsular contracture: Formation of scar tissue around the implant, which can cause hardness or distortion.
7. How long does the prosthesis last?
Testicular prostheses are designed to be durable and long-lasting. While they do not have a set lifespan, they typically do not need to be replaced unless complications arise or if the patient desires a different size or type.
8. Can the prosthesis be felt during physical activity?
Most men report that the prosthesis feels natural and does not interfere with normal physical activities, including sports and sexual intercourse. Over time, many men forget they even have the prosthesis.
9. What is the recovery process like?
- Immediate post-surgery: Patients are usually able to go home the same day or the following day. Pain and swelling are common and can be managed with pain medication.
- First few weeks: Activities that strain the groin area should be avoided. Patients should follow their doctor’s instructions regarding hygiene and wound care.
- Long-term: Regular check-ups may be necessary to ensure the prosthesis remains in place and no complications develop.
10. How do I choose the right prosthesis?
Choosing the right prosthesis involves consultation with a urologist who will consider factors such as:
- Size and shape of the remaining testicle (if present).
- Patient’s body size and preference.
- Material and type of prosthesis preferred.
11. Contraindications for a testicular prosthesis include:
- Active Infection: Implantation should be avoided if there is an ongoing infection in the scrotum or surrounding areas to prevent further complications.
- Compromised Immune System: Patients with severe immunodeficiency or ongoing immunosuppressive therapy may be at higher risk for infection and complications.
- Poor Surgical Candidate: Patients with significant comorbidities or those who cannot tolerate anesthesia or surgery due to their health status may not be suitable candidates.
- Severe Scarring or Tissue Damage: Extensive scarring or damage in the scrotal area might make implantation difficult or increase the risk of complications.
- Allergic Reactions: Known allergy to silicone or any materials used in the prosthesis.
- Uncontrolled Diabetes: Poorly controlled diabetes can impair wound healing and increase the risk of infection.
- Psychological Unsuitability: Patients with significant psychiatric conditions that might affect their perception of the prosthesis or adherence to post-surgical care.
It’s essential for individuals considering a testicular prosthesis to consult with their urologist to assess their specific situation and determine if any contraindications apply.
12. Which age is good for testicular prosthesis implantation?
There isn’t a specific age range considered “ideal” for testicular prosthesis implantation. The decision is typically based on individual circumstances and medical recommendations. Generally, the procedure is considered appropriate for adult men who have completed their physical development. Factors that may influence the timing include:
- Completion of Growth: It’s advisable to wait until the testicles have fully developed, typically by late adolescence or early adulthood.
- Stable Health Condition: The patient should be in overall good health without significant medical conditions that could complicate surgery or recovery.
- Psychological Readiness: The patient should be emotionally prepared to undergo the procedure and understand the implications of having a testicular prosthesis.
- Personal Preference: Timing may also be influenced by personal preferences and the impact on quality of life and body image.
Summary
A testicular prosthesis is an artificial implant used to replace a missing testicle, often due to injury, disease, or surgery. It is typically made of silicone and aims to restore the scrotum’s natural appearance. The implantation procedure is relatively simple, with most men experiencing minimal complications and a quick recovery. Benefits include improved cosmetic appearance and self-esteem. Risks are generally low but can include infection and implant rejection. For detailed advice and options, consulting with a urologist is recommended.
Prof. Dr. Emin ÖZBEK
Urologist
Istanbul- TURKIYE



Leave a Reply