Priapism is a urological condition characterized by a prolonged and often painful erection that persists beyond or is unrelated to sexual arousal. If left untreated, it can lead to permanent erectile dysfunction due to tissue damage. Treatment options vary based on the underlying cause and severity, ranging from medication to surgical intervention. In cases where priapism results in severe erectile dysfunction, penile prosthesis implantation surgery may be considered. Penile prostheses are typically recommended when other treatments have failed, offering a reliable solution for restoring sexual function and improving quality of life.
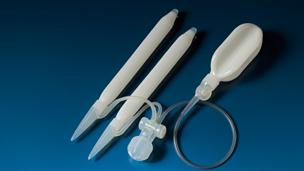
Indications of penile prosthesis surgery in priapism
Here are the main indications for penile prosthesis implantation in patients who have experienced priapism:
- Ischemic Priapism: When ischemic priapism (low-flow priapism) leads to irreversible damage to the erectile tissue, resulting in fibrosis and permanent erectile dysfunction, a penile prosthesis may be indicated to restore erectile function.
- Recurrent Priapism: For patients who experience frequent episodes of priapism that cannot be adequately managed with conservative treatments or medications, penile prosthesis implantation can offer a long-term solution to prevent further episodes and the potential for subsequent tissue damage.
- Failure of Conservative Treatments: If medical and less invasive surgical treatments, such as aspiration and irrigation or shunt procedures, fail to resolve priapism effectively or lead to satisfactory outcomes in terms of erectile function, prosthesis implantation may be considered.
- Psychological Impact: For patients who suffer significant psychological distress or quality-of-life impairment due to the inability to achieve or maintain an erection following episodes of priapism, a penile prosthesis can provide relief and improve sexual confidence.
- Post-Thrombosis Fibrosis: In cases where priapism is associated with conditions that lead to thrombosis and subsequent fibrosis (such as sickle cell disease), resulting in loss of erectile function, prosthesis implantation can help overcome these complications.
- Chronic Priapism with Erectile Dysfunction: Chronic or stuttering priapism that leads to persistent erectile dysfunction despite treatment may be an indication for prosthesis implantation to restore functionality.
Early or late penile prosthesis implantation
The timing of penile prosthesis implantation surgery in the context of priapism can significantly impact outcomes and is generally categorized into early and late implantation. Each approach has its advantages and considerations:
Early Penile Prosthesis Implantation
Advantages:
- Preservation of Penile Length and Anatomy: Early implantation, typically within weeks to a few months after the resolution of priapism, can help preserve penile length and anatomy, minimizing the degree of tissue fibrosis and shortening that can occur over time.
- Reduced Risk of Fibrosis: Implanting the prosthesis early, before significant fibrosis and scarring develop, can make the surgery technically easier and reduce the risk of complications related to severe fibrotic changes.
- Faster Restoration of Sexual Function: Early implantation can lead to a quicker return to sexual activity, which can be important for the patient’s psychological well-being and quality of life.
Considerations:
- Patient Readiness: The patient must be psychologically ready to undergo surgery and accept the implications of having a penile prosthesis.
- Infection Risk: As with any surgery, there is a risk of infection, which needs to be carefully managed.
Late Penile Prosthesis Implantation
Advantages:
- Time for Conservative Treatment: Delaying implantation allows time to explore and exhaust less invasive treatment options, such as medications or shunt procedures, to see if erectile function can be restored without surgery.
- Reduced Immediate Surgery Pressure: Some patients may prefer to delay surgery to mentally and emotionally prepare for the procedure.
Considerations:
- Increased Risk of Fibrosis: Delaying the procedure increases the risk of extensive fibrotic changes, making the surgery more complex and potentially affecting the outcomes, such as decreased penile length and function.
- Technical Difficulty: The presence of severe fibrosis can make surgical dissection and implantation more challenging, potentially increasing the risk of complications and less favorable outcomes.
- Prolonged Erectile Dysfunction: Delaying the surgery can prolong the period of erectile dysfunction, which can negatively impact the patient’s quality of life and psychological health.
Decision-Making
The decision between early and late penile prosthesis implantation should be individualized, taking into account factors such as:
- Severity and Duration of Priapism: More severe or prolonged cases may benefit from early intervention to prevent further damage.
- Extent of Erectile Dysfunction: Patients with significant and persistent erectile dysfunction may opt for earlier surgery.
- Patient Preferences and Goals: The patient’s personal goals, expectations, and readiness for surgery should play a central role in the decision-making process.
- Medical and Psychological Assessment: A thorough assessment by a urologist and possibly a mental health professional can help guide the timing of the surgery.
Which type of penile prosthesis is preferred in priapism?
The two main types of penile prostheses are malleable (or semi-rigid) and inflatable prostheses, each with its own advantages and considerations:
Malleable (Semi-rigid) Penile Prosthesis
Advantages:
- Simplicity: Malleable prostheses are simpler in design and easier to implant, especially in cases with significant fibrosis due to priapism. They consist of bendable rods that allow the penis to be positioned as needed.
- Lower Risk of Mechanical Failure: Because they have no mechanical parts, malleable prostheses have a lower risk of malfunction and require less follow-up care.
- Suitable for Severe Fibrosis: They are often preferred in cases with extensive fibrosis, as they can be easier to place in scarred tissue.
- Cost-Effective: Malleable prostheses are generally less expensive than inflatable ones, which can be an important consideration for some patients.
Considerations:
- Cosmetic Appearance: The penis remains semi-rigid at all times, which may not be ideal for all patients in terms of appearance and comfort.
- Lack of Flaccidity: Patients may feel less satisfied with the inability to achieve a fully flaccid state.
Inflatable Penile Prosthesis
Advantages:
- Natural Erection Simulation: Inflatable prostheses can provide a more natural-looking erection and flaccidity, which many patients find more aesthetically pleasing and comfortable.
- Better Patient Satisfaction: Many patients report higher satisfaction due to the ability to control when the penis is erect or flaccid.
- Enhanced Sexual Function: Inflatable prostheses may provide better rigidity and a more natural feel during intercourse.
Considerations:
- Complexity and Risk of Mechanical Failure: Inflatable prostheses are more complex and have a risk of mechanical failure, which may require additional surgery to repair or replace.
- Technical Challenges: The surgery is more technically demanding, particularly in patients with severe fibrosis from priapism.
- Higher Cost: They are typically more expensive than malleable prostheses, which can be a consideration for some patients.
Decision-Making
The choice between a malleable and an inflatable prosthesis should be based on a comprehensive evaluation that includes:
- Degree of Fibrosis: In cases with severe fibrosis, a malleable prosthesis might be more practical.
- Patient Preference: Patients who prioritize a natural appearance and are comfortable with managing an inflatable device may prefer this option.
- Lifestyle and Manual Dexterity: Inflatable prostheses require manual dexterity to operate the pump, which might be a factor for some patients.
- Cost and Availability: Economic factors and the availability of different prosthesis types might influence the decision.
Risks of penile prosthesis surgery in priapism
Penile prosthesis implantation surgery in patients with priapism carries certain risks and potential complications, as with any surgical procedure. Here are some of the primary risks associated with penile prosthesis implantation in the context of priapism:
Surgical Risks
- Infection: Infection is a significant risk, particularly because of the prosthesis being a foreign body. This risk is heightened in patients with priapism due to compromised blood flow and tissue health.
- Bleeding and Hematoma: There is a risk of bleeding during or after the surgery, which can lead to hematoma formation. This may require further intervention to resolve.
- Anesthetic Complications: As with any surgery, there are risks related to anesthesia, including allergic reactions and respiratory issues.
Prosthesis-Related Risks
- Mechanical Failure: Inflatable prostheses have moving parts that can fail over time, potentially requiring additional surgery for repair or replacement.
- Erosion and Extrusion: The prosthesis can erode through the skin or other tissues, or even extrude from the body. This is more likely if the tissue is already compromised due to fibrosis from priapism.
- Malposition or Migration: The prosthesis might not stay in the correct position or could migrate, which might necessitate further surgery to correct.
Functional Risks
- Loss of Penile Length: Scar tissue and fibrosis from priapism can lead to a loss of penile length, which the prosthesis cannot fully restore.
- Altered Sensation: Some patients may experience changes in penile sensation, which can affect sexual satisfaction.
- Unsatisfactory Cosmetic or Functional Outcome: There is a risk that the prosthesis may not meet the patient’s expectations in terms of cosmetic appearance or functional performance.
Psychological Risks
- Emotional and Psychological Impact: Adjusting to a penile prosthesis can be emotionally challenging for some patients, impacting self-esteem and body image.
- Partner Acceptance: There may be concerns about how a sexual partner perceives the prosthesis, which can affect intimate relationships.
Considerations
- Preoperative Counseling: Comprehensive counseling about the potential risks and benefits of the surgery, as well as realistic expectations, is crucial.
- Surgeon Expertise: Choosing a surgeon with significant experience in penile prosthesis implantation, particularly in complex cases such as those involving priapism, can help minimize risks.
- Postoperative Care: Adhering to postoperative care instructions, including infection prevention strategies and follow-up appointments, is vital for minimizing complications.
Summary
Priapism is a medical condition characterized by a prolonged, often painful erection that persists beyond or is unrelated to sexual stimulation. If untreated, it can lead to permanent erectile dysfunction due to tissue damage. In cases where priapism results in severe erectile dysfunction, penile prosthesis implantation surgery may be considered. There are two main types of prostheses: malleable and inflatable. The choice depends on factors such as the degree of fibrosis, patient preferences, and cost considerations. Surgery carries risks, including infection, mechanical failure, and changes in penile sensation. However, it can significantly improve quality of life for patients with priapism-related erectile dysfunction. Thorough evaluation and counseling are crucial to ensure optimal outcomes. We prefere early penile prosthesis implantation.
Prof. Dr. Emin ÖZBEK
Urologist
Istanbul- TURKIYE



Leave a Reply