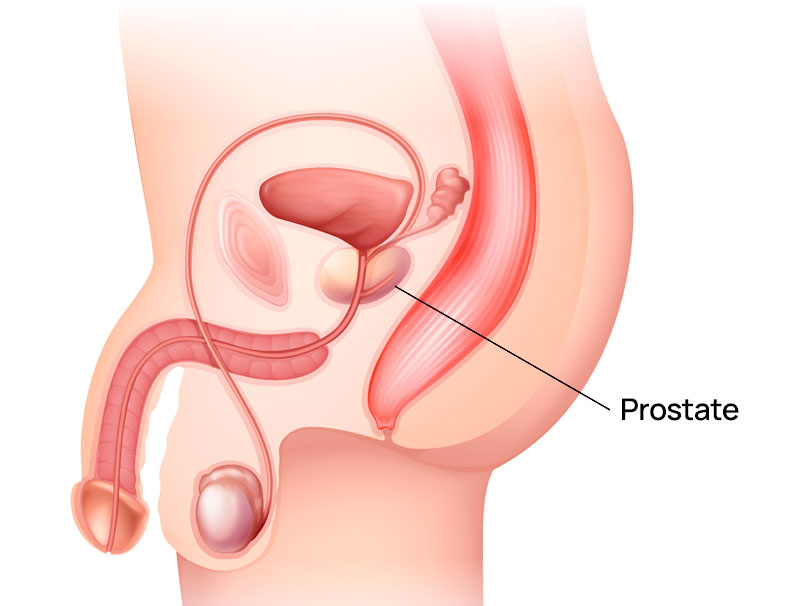
Prostate health is an important aspect of men’s health, particularly for those over the age of 50. The prostate is a small, walnut-sized gland located below the bladder and in front of the rectum. It plays a crucial role in male reproductive health by producing seminal fluid, which nourishes and transports sperm.
Regular prostatic check-ups are essential for early detection and prevention of prostate-related issues such as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), prostatitis, and prostate cancer. Prostate cancer is one of the most common cancers in men, but early detection through screening can lead to more effective treatment and better outcomes.
Maintaining prostate health can involve a healthy diet, regular exercise, and managing risk factors such as obesity and smoking. Regular screenings are crucial, especially for those with a family history of prostate cancer or other risk factors.
What is “prostate health?”
Prostate health refers to the well-being and proper functioning of the prostate gland, a key component of the male reproductive system. It encompasses the prevention, early detection, and management of various prostate-related conditions and diseases. Maintaining prostate health is crucial for overall male health, particularly as men age.
Normal Prostate Function:
- The prostate produces seminal fluid, which combines with sperm to form semen.
- It plays a role in regulating urine flow by exerting pressure on the urethra.
Common Prostate Issues:
- BPH: A non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate, common in older men, which can cause urinary problems.
- Prostatitis: Inflammation of the prostate, which can be acute or chronic and may cause pain and urinary issues.
- Prostate Cancer: One of the most common cancers in men, especially those over the age of 50.
Symptoms of Prostate Problems:
- Blood in urine or semen
- Difficulty urinating or a weak urine stream
- Frequent urination, especially at night
- Pain or discomfort in the pelvic area
- Painful ejaculation
Prostate Health Maintenance:
- Regular Check-ups: Routine screenings like Digital Rectal Exams (DRE) and Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) tests are essential for early detection of prostate issues.
- Healthy Lifestyle: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats, regular exercise, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol can support prostate health.
- Hydration: Adequate water intake helps maintain urinary health.
- Medical Consultation: Seeking medical advice for any urinary or reproductive symptoms.
Screening and Diagnosis:
- DRE: A physical exam where a doctor feels the prostate through the rectum to check for abnormalities.
- PSA Test: A blood test measuring the level of PSA, an indicator of prostate health.
- Imaging: Ultrasound or MRI for detailed views of the prostate.
- Biopsy: Taking a tissue sample for analysis if abnormalities are found.
Check up for ptostate health
A prostate health check-up is a crucial part of maintaining overall male health, especially as men age. These check-ups help in the early detection and management of prostate-related issues such as BPH, prostatitis, and prostate cancer. Here’s what a typical prostate health check-up involves:
Components of a Prostate Health Check-up:
Medical History:
- Personal and Family History: Discuss any symptoms, medical history, and family history of prostate issues or cancers.
Physical Examination:
- Digital Rectal Exam (DRE): A doctor inserts a gloved, lubricated finger into the rectum to feel the prostate gland. The exam checks for size, shape, and any abnormalities like lumps or hard areas.
Laboratory Tests:
- PSA Test: A blood test measures the level of PSA, a protein produced by the prostate. Elevated levels can indicate prostate enlargement, inflammation, or cancer.
- Urinalysis: A urine test checks for signs of infection or other conditions affecting the urinary tract.
Imaging Tests:
- Transrectal Ultrasound (TRUS): An ultrasound probe inserted into the rectum provides images of the prostate to assess its size and detect abnormalities.
- MRI: Magnetic Resonance Imaging provides detailed images of the prostate and surrounding tissues, useful for detecting and staging prostate cancer.
Biopsy (if needed):
- If DRE, PSA, or imaging tests indicate potential issues, a biopsy may be performed. A small sample of prostate tissue is taken and examined for cancer cells.
Frequency of Check-ups:
- Men aged 50 and above: Annual check-ups are generally recommended.
- Men with higher risk factors: Those with a family history of prostate cancer or of African descent may need to start check-ups earlier, around age 40-45.
What is importance of “prostate check up?”
Prostate check-ups are important for several reasons, particularly for men over the age of 50 or those with risk factors for prostate issues. Here are the key reasons:
Early Detection of Prostate Cancer
- Prostate cancer is one of the most common types of cancer in men. Early-stage prostate cancer often has no symptoms, so regular check-ups can help detect it at an early and more treatable stage.
Monitoring Prostate Health
- Regular check-ups can help monitor the size and condition of the prostate gland, identifying issues like BPH, which is a non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate that can cause urinary problems.
Screening for Prostatitis
- Prostatitis, or inflammation of the prostate gland, can cause discomfort and urinary issues. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications and improve quality of life.
Reducing Mortality
- Early detection and treatment of prostate issues, including cancer, can significantly reduce the risk of complications and mortality.
Personalized Medical Advice
- Regular check-ups provide an opportunity for urologists to offer personalized advice on lifestyle changes, dietary adjustments, and other preventive measures to maintain prostate health.
Risk factors: Who need regular prostate check-up?
Regular prostate check-ups are essential for maintaining prostate health and catching potential issues early when they are most treatable. Here are the groups who need to consider regular prostate screening:
Men Over 50
- Age is a significant risk factor for prostate issues, including prostate cancer. Men over the age of 50 are generally advised to start regular prostate screenings.
Men with a Family History of Prostate Cancer
- Men with a family history of prostate cancer, especially if a father or brother was diagnosed, are at higher risk and may need to start screenings earlier, often around age 40-45.
African American Men
- African American men have a higher risk of developing prostate cancer and are more likely to develop it at a younger age and have a more aggressive form. Regular screenings may need to start earlier, around age 45.
Men with Certain Genetic Predispositions
- Men with certain genetic mutations, such as BRCA1 or BRCA2, are at higher risk for prostate cancer. These individuals should discuss with their healthcare provider when to start screenings.
Men with Symptoms of Prostate Issues
- Men experiencing urinary symptoms (e.g., frequent urination, difficulty starting or stopping urination, weak urine flow, or pain during urination) should have their prostate health checked regardless of age.
Men with Other Risk Factors
- Men with other risk factors like a high-fat diet, obesity, and exposure to certain chemicals may also need regular check-ups.
Frequency of check-ups for prostate
The frequency of prostate check-ups depends on a man’s age, risk factors, and overall health. Here are general guidelines:
Average Risk
- Ages 50-70: Men at average risk should have a prostate check-up every 2 years. This often includes a PSA test and possibly a DRE.
Higher Risk
- Family History of Prostate Cancer: Men with a first-degree relative (father or brother) diagnosed with prostate cancer should start screenings at age 45 and have them annually.
- African American Men: Should start screenings at age 45 and have them annually due to a higher risk of developing prostate cancer.
- Genetic Predispositions: Men with known BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations or other significant genetic predispositions should discuss a personalized screening schedule with their urologist, often starting at age 40-45 and having annual check-ups.
Men with Symptoms
- Men of any age experiencing urinary symptoms (e.g., frequent urination, difficulty starting or stopping urination, weak urine flow, or pain during urination) should seek medical advice and may require immediate and possibly more frequent check-ups.
After an Abnormal Result
- If a previous check-up reveals elevated PSA levels or abnormalities during a DRE, follow-up screenings might be scheduled more frequently, such as every 3-6 months, depending on the findings and recommendations from the urologist.
Older Men
- Ages 70 and Above: The necessity of continued screening should be based on overall health and life expectancy. Some guidelines suggest that men over 70 or those with less than 10-15 years of life expectancy may not need regular screening.
Personalized Schedule
- Always discuss personal and family medical history with a urologist to determine the most appropriate screening schedule. Personalized schedules may vary based on individual health conditions and risk factors.
Summary
Prostate health refers to the well-being of the prostate gland, which is vital for male reproductive health. Common issues include BPH, prostatitis, and prostate cancer. Regular prostatic check-ups are crucial for early detection and effective management of these conditions. A typical check-up involves:
- DRE: A physical examination to feel for abnormalities.
- PSA Test: A blood test measuring PSA levels.
- Imaging Tests: Ultrasound or MRI for detailed views.
- Biopsy: Tissue sampling if abnormalities are found.
Maintaining prostate health includes a balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol. Regular screenings, especially for men over 50 or those with higher risk factors, are essential for preventing serious prostate issues.
Prof. Dr. Emin ÖZBEK
Urologist
Istanbul- TURKIYE



Leave a Reply