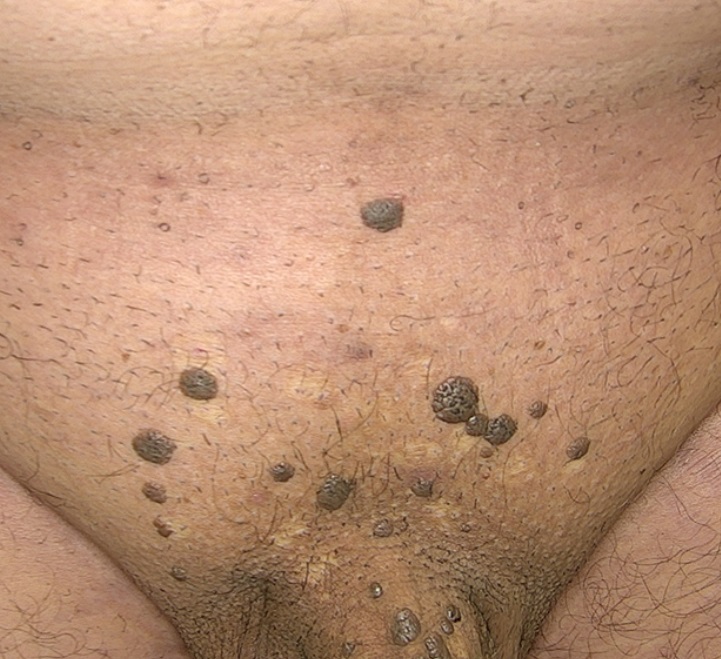
Cauterization, or cotherisation, is a medical procedure used to remove HPV (Human Papillomavirus) warts by burning the tissue with heat, electricity, or chemicals. Genital HPV is a common sexually transmitted infection that can cause genital warts, known as condylomas. These warts appear as small, flesh-colored or gray growths in the genital area.
What is genital HPV cauterization?
Genital HPV Cauterization is a medical procedure used to remove genital warts caused by the HPV. These warts, also known as condylomas, can appear in the genital or anal areas and are often associated with certain strains of HPV. Cauterization involves burning the wart tissue to destroy it, which can help prevent the spread of the virus and reduce the risk of recurrence.
Cauterization is generally effective, but it may not completely eliminate HPV from the body. The virus can remain dormant and may cause future outbreaks.
How to do HPV cauterization?
This procedure is usually performed under local anesthesia and under office conditions.
- Preparation: The patient may be given a local anesthetic to numb the area and minimize discomfort during the procedure. The area around the wart is cleaned to reduce the risk of infection.
- Procedure:
- Electrocauterization: This method uses a small, heated electrical probe to burn off the warts. The heat generated by the electrical current destroys the wart tissue.
- Chemical Cauterization: In this method, a chemical solution (such as trichloroacetic acid) is applied to the wart, causing it to burn and disintegrate.
- Thermal Cauterization: A heated instrument, such as a cautery pen, is used to directly burn off the wart.
- Post-Procedure Care: The treated area may be covered with a dressing to protect it as it heals. Patients are advised to keep the area clean and dry, avoid sexual activity until the area is fully healed, and follow any additional care instructions provided by their healthcare provider. Pain relievers may be recommended to manage any discomfort following the procedure.
- Follow-Up: A follow-up visit may be scheduled to ensure proper healing and check for any recurrence of warts.
- Procedure:
Complications
While genital HPV cauterization is generally a safe and effective procedure, it can have some potential complications. Here are some possible complications:
- Pain and Discomfort: Little pain possible during and after the grocedure.
- Infection: The treated area is at risk of infection, particularly if the wound is not properly cared for. Signs of infection include increased redness, swelling, warmth, pus, and fever.
- Scarring: Cauterization can lead to scarring at the site of the treated warts. The extent of scarring depends on the depth of the cauterization and individual healing responses. Some patients may develop hypertrophic scars or keloids, which are raised, thickened scars that can be cosmetically concerning.
- Bleeding: Minor bleeding during or after the procedure is common, but in some cases, significant bleeding can occur, especially if larger warts are treated.
- Recurrence of Warts: While cauterization removes visible warts, it does not eliminate the underlying HPV infection. This means that warts can recur, sometimes requiring further treatment.
- Altered Sensation: Nerve damage during the procedure can lead to altered sensation in the treated area, such as numbness, tingling, or hypersensitivity. In most cases, this is temporary, but it can be permanent in rare instances.
- Delayed Healing: Some patients may experience delayed healing of the treated area, which can prolong discomfort and increase the risk of infection or scarring. Factors such as poor circulation, underlying health conditions (e.g., diabetes), or smoking can contribute to delayed wound healing.
- Pigment Changes: Cauterization can cause changes in skin pigmentation at the treatment site, leading to either hypopigmentation (lighter skin) or hyperpigmentation (darker skin). These changes can be temporary or permanent.
- Adverse Reactions to Anesthesia: Some patients may experience allergic reactions or adverse effects from the local anesthesia used during the procedure. This is rare but possible.
- Psychological Impact: The procedure and its after-effects, such as scarring or recurrence, can cause emotional or psychological stress, particularly if the warts are located in highly sensitive or visible areas.
Advantages of cauterization
Genital HPV cauterization offers several advantages as a treatment option for removing genital warts. Here are the key benefits:
- Effective Removal of Warts: Immediate Results and high Success Rate
- Versatility: Suitable for Various Locations and adaptable to aart size
- Prevention of Spread: By removing visible warts, cauterization can help reduce the likelihood of spreading HPV to sexual partners, contributing to better sexual health and potentially lowering the risk of transmission.
- Long-Lasting Results: Although recurrence of warts is possible, cauterization often provides long-lasting results, especially when combined with other treatments or lifestyle changes that boost the immune system.
- Minimal Systemic Side Effects: Unlike some oral or topical treatments that may have systemic effects, cauterization is a localized procedure, which means it typically does not affect other parts of the body.
- No Need for Ongoing Medication: For many patients, cauterization can be a one-time procedure, eliminating the need for continuous application of topical medications or repeated visits for other treatments.
- Cost-Effectiveness: In some cases, cauterization can be more cost-effective than other treatment options, especially if it successfully removes the warts in a single session.
- Low Risk of Complications: When performed by a trained healthcare provider, cauterization is generally safe, with a low risk of severe complications.
- Aesthetic Improvement: By removing unsightly warts, cauterization can improve the aesthetic appearance of the genital area, which can boost self-esteem and reduce psychological distress associated with the presence of warts.
- Quick Recovery Time: Compared to some other surgical methods, cauterization often has a relatively quick recovery time, allowing patients to resume normal activities sooner.
Summary
The procedure is effective in providing immediate removal of visible warts, reducing the spread of HPV, and offering long-lasting results. It is generally safe and has a quick recovery time. Cauterization is a versatile option suitable for various wart sizes and locations, making it a valuable treatment choice for managing genital warts.
Prof. Dr. Emin ÖZBEK
Urologist
Istanbul- TURKIYE



Leave a Reply